Zustand 는 React 애플리케이션의 상태 관리를 간편하게 해주는
라이브러리 입니다.
Zustand 는 상태 관리를 위해 React 의 Context API 와 함께 사용되며,
Redux 와 비슷한 기능을 제공하지만 훨씬 간단하고 직관적입니다.
특징
간단한 API
Zustand 는 간단하고 직관적인 API 를 제공하여 상태를 관리합니다.
create 함수를 사용하여 상태를 초기화하고, 이를 통해 상태를 업데이트하고 구독할 수 있습니다.
Hooks 기반
Zustand 는 React Hooks 와 함께 사용되어 React 애플리케이션의 상태를 관리합니다.
이는 함수형 컴포넌트에서 상태를 쉽게 관리할 수 있음을 의미합니다.
최적화
Zustand 는 내부적으로 Immer 라이브러리를 사용하여 불변성을 유지하면서 상태를 업데이트합니다.
또한 컴포넌트이 렌더링을 최적화하기 위해 쿼리 기반의 구독을 지원합니다.
편리한 디버깅
Zustand 는 상태의 변화를 추적하고 디버깅할 수 있는 도구를 제공합니다.
DevTools 확장 프로그램을 사용하여 상태의 변화를 모니터링하고 디버깅할 수 있습니다.
Zustand 와 Redux 의 차이점
API 및 사용법
Redux : 강력하고 유연한 상태 관리 도구이지만, 사용법이 비교적 복잡합니다.
Zustand : Redux 보다 훨씬 간단한 API 를 제공합니다.
파일 크기
Redux : 라이브러리 자체와 함께 사용하는 추가적인 미들웨어 및 도구들 때문에 번들 크기가 커질 수 있습니다.
Zustand : 훨씬 작고 경량화된 라이브러리입니다. 번들 크기가 작고 성능 면에서도 더 유리할 수 있습니다.
불변성 유지
Redux : 불변성을 유지하려면 개발자가 신경써서 개발을 해야 합니다.
Zustand : 내부적으로 Immer 와 함께 사용되어 불변성을 자동으로 유지해 개발자가 신경쓰지 않아도 됩니다.
React 와의 통합
Redux: Redux 는 React 와 함께 사용할 때 별도의 라이브러리인 react-redux 를 사용해야 합니다. 이는 별도의 작업을 의미합니다.
Zustand: React Hooks 와 함께 사용되며, 별도의 라이브러리 없이 React 컴포넌트와 상태를 직접 연결할 수 있습니다.
Zustand 는 작은 규모의 프로젝트나 단순한 상태 관리에 적합합니다.
Redux 는 대규모 애플리케이션에 더 적합하며, 상태 관리에 대한 엄격한 규칙과 고도의 유연성이 필요한 경우 적합합니다.
설치 및 실행
설치
npm install zustand실행
get, set 함수를 사용
import { create } from "zustand";
type CountState = {
count: number;
increase: () => void;
decrease: () => void;
}
export const useCountStore = create<CountState>((get,set) => ({
count: 1,
increase: () => {
const { count } = get();
set({count: count + 1});
},
decrease: () => {
const { count } = get();
set({count: count - 1});
},
}))
set 함수만 사용
import { create } from "zustand";
type CountState = {
count: number;
increase: () => void;
decrease: () => void;
};
export const countStateStore = create<CountState>(set => ({
count: 1,
increase: () => set(state => ({count: state.count + 1})),
decrease: () => set(state => ({count: state.count - 1}))
}));
생성한 스토어를 다음과 같이 컴포넌트에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
import './App.css'
import {useCountStore, useCountStore2} from './store/zustand'
function App() {
// 첫번째 사용법
const { count } = useCountStore();
const { increase } = useCountStore();
// 두번째 사용법
const count = useCountStore(state => state.count);
const increase = useCountStore(state => state.increase);
// 세번째 사용법
const {count, increase, decrease} = useCountStore();
return (
<>
<div>
<span>{count}</span>
<button onClick={increase}>one Up</button>
</div>
</>
)
}
export default App
단순하게 1씩 증가하는 로직이 아니라 동적인 값에 따라 증가하는 값이 다르게 만들고 싶다면 함수에 인자값을 넣어주시면 됩니다.
아래의 예시 코드는 동적인 값에 따라 증가하는 값이 다른 예제 입니다.
import { create } from "zustand";
type CountState = {
count: number;
increase: (value?: number) => void;
decrease: () => void;
};
export const countStateStore = create<CountState>((get,set) => ({
count: 1,
increase: (value = 1) => set(state => ({count: state.count + value})),
decrease: () => set(state => ({count: state.count - 1}))
}));
// 이렇게 설정하면
onClick = {() => increase(10)} ... 해주면 됩니다.
액션 분리
만약 여러 컴포넌트에서 단일 스토어의 액션을 많이 사용한다면, 액션을 분리해 관리하는 패턴도 활용해 보시는 것을 추천합니다.
다음과 같이 actions 객체 안에서 모든 액션을 관리하면, 각 컴포넌트에서 필요한 액션만 가져오기 쉽습니다.
import { create } from 'zustand'
type CountState = {
count: number;
actions: {
increase: () => void;
decrease: () => void;
}
}
export const useCountStore = create<CountState>(set => ({
count: 0,
actions: {
increase: () => set(state => ({count: state.count + 1})),
decrease: () => set(state => ({count: state.count - 1}))
}
}))import './App.css'
import {useCountStore} from './store/count'
function App() {
const {count} = useCountStore();
const {increase, decrease} = useCountStore(state => state.actions);
return (
<>
<div>
<span>{count}</span>
<button onClick={increase}>increase</button>
<button onClick={decrease}>increase</button>
</div>
</>
)
}
export default App
상태 초기화
만약 상태를 초깃값으로 되돌리는 기능이 필요한 경우, 다음과 같이 resetState 함수를 추가해 사용할 수 있습니다.
액션을 제외한 상태만 초기화 하는 것이니, 상태와 액션을 분리해서 타입과 초깃값을 작성해야 합니다.
import { create } from 'zustand'
interface State {
count: number;
double: number;
min: number;
max: number;
}
interface Actions {
actions: {
increase: () => void;
decrease: () => void;
resetState: () => void;
}
}
const initialState: State = {
count: 1,
double: 2,
min: 0,
max: 10
}
export const useCountStore = create<State & Actions>(set => ({
...initialState,
actions: {
increase: () => set(state => ({count: state.count + 1})),
decrease: () => set(state => ({count: state.count - 1})),
resetState: () => set(initialState)
}
}))import './App.css'
import {useCountStore} from './store/count'
function App() {
const {count, double, min, max} = useCountStore();
const {increase, decrease, resetState} = useCountStore(state => state.actions);
return (
<>
<div>
<span>count - {count}</span>
<span>double - {double}</span>
<span>min - {min}</span>
<span>max - {max}</span>
<button onClick={increase}>increase</button>
<button onClick={decrease}>increase</button>
<button onClick={resetState}>reset</button>
</div>
</>
)
}
export default App
만약 전부 초기화 시키고 싶지 않고 특정 값만 초기화 하고 싶다면 아래의 코드처럼 바꾸어 주시면 됩니다.
import { create } from 'zustand'
interface State {
count: number;
double: number;
min: number;
max: number;
}
interface Actions {
actions: {
increase: () => void;
decrease: () => void;
resetState: (keys?: Array<keyof State>) => void;
}
}
const initialState: State = {
count: 1,
double: 2,
min: 0,
max: 10
}
export const useCountStore = create<State & Actions>(set => ({
...initialState,
actions: {
increase: () => set(state => ({count: state.count + 1})),
decrease: () => set(state => ({count: state.count - 1})),
resetState: keys => {
if (!keys) {
set(initialState)
return
}
keys.forEach(key => {
set(({[key] : initialState[key]}))
})
}
}
}))import './App.css'
import {useCountStore} from './store/count'
function App() {
const {count, double, min, max} = useCountStore();
const {increase, decrease, resetState} = useCountStore(state => state.actions);
return (
<>
<div>
<span>count - {count}</span>
<span>double - {double}</span>
<span>min - {min}</span>
<span>max - {max}</span>
<button onClick={increase}>increase</button>
<button onClick={decrease}>increase</button>
<button onClick={() => resetState()}>reset</button>
<button onClick={() => resetState(['double', 'max'])}>reset</button>
</div>
</>
)
}
export default App
미들 웨어
Zustand 는 미들웨어 라는 것을 사용하여, 스토어의 추가 기능(타입추론, 중첩 객체 변경 등) 을 확장할 수 있습니다.
즉 불필요한 코드를 줄이고 코드 가독성을 높일 수 있는 방법이기도 합니다.
상태의 타입 추론
타입스크립트를 사용할 때, 상태 타입을 직접 작성하지 않고 추론하도록 combine 이라는 미들웨어를 사용할 수 있습니다.
combine 미들웨어는 첫 번째 인수로 추론할 상태를 받고, 두 번째 인수로 set, get 매개변수를 포함하는 액션 함수를 받습니다.
import { create } from 'zustand'
import { combine } from 'zustand/middleware';
const initialState = {
count: 1,
double: 2,
min: 0,
max: 10
}
export const useCountStore = create(
combine(
initialState,
set => ({
actions: {
increase: (value = 1) => set(state => ({count: state.count + value})),
decrease: () => set(state => ({count: state.count - 1})),
resetState: (keys?: Array<keyof typeof initialState>) => {
if (!keys) {
set(initialState)
return
}
keys.forEach(key => {
set(({[key] : initialState[key]}))
})
}
}
})
)
)
액션 호출 in 액션
액션 함수 내부에서 다른 액션을 호출할 때, get() 함수의 반환으로 액션을 가져와 호출할 수 있습니다.
하지만, combine 미들웨어를 사용하면, get() 함수가 액션 타입을 추론하지 못합니다.
따라서 아래처럼 만들어 주시면 combine 에서도 액션 함수 내부에 다른 액션을 호출할 수 있게 됩니다.
// ...
export const useCountStore = create(
combine(
initialState,
set => {
function increase() {
set(state => ({ count: state.count + 1 }))
increaseDouble() // OK!
}
function increaseDouble() {
set(state => ({ double: state.count * 2 }))
}
return {
actions: {
increase,
increaseDouble
}
}
}
)
)
스토리지 사용 (Persist)
Zustand 는 persist 미들웨어를 사용해 스토리지에 상태를 저장하고 불러올 수 있습니다.
이를 통해 페이지를 새로고침하거나 다시 방문했을 때에도 상태를 유지할 수 있습니다.
type CountState = {
number: number;
increaseNumber: () => void;
decreaseNumber: () => void;
};
// Zustand 스토어 생성
export const countStateStore = create<CountState>()(
persist(
(set) => ({
number: 1,
increaseNumber: () => set((state) => ({ number: state.number + 1 })),
decreaseNumber: () => set((state) => ({ number: state.number - 1 })),
}),
{
name: "number-storage", // 로컬 스토리지에 저장될 key 이름
getStorage: () => localStorage, // 로컬 스토리지 사용
} as PersistOptions<CountState> // PersistOptions 타입 명시
)
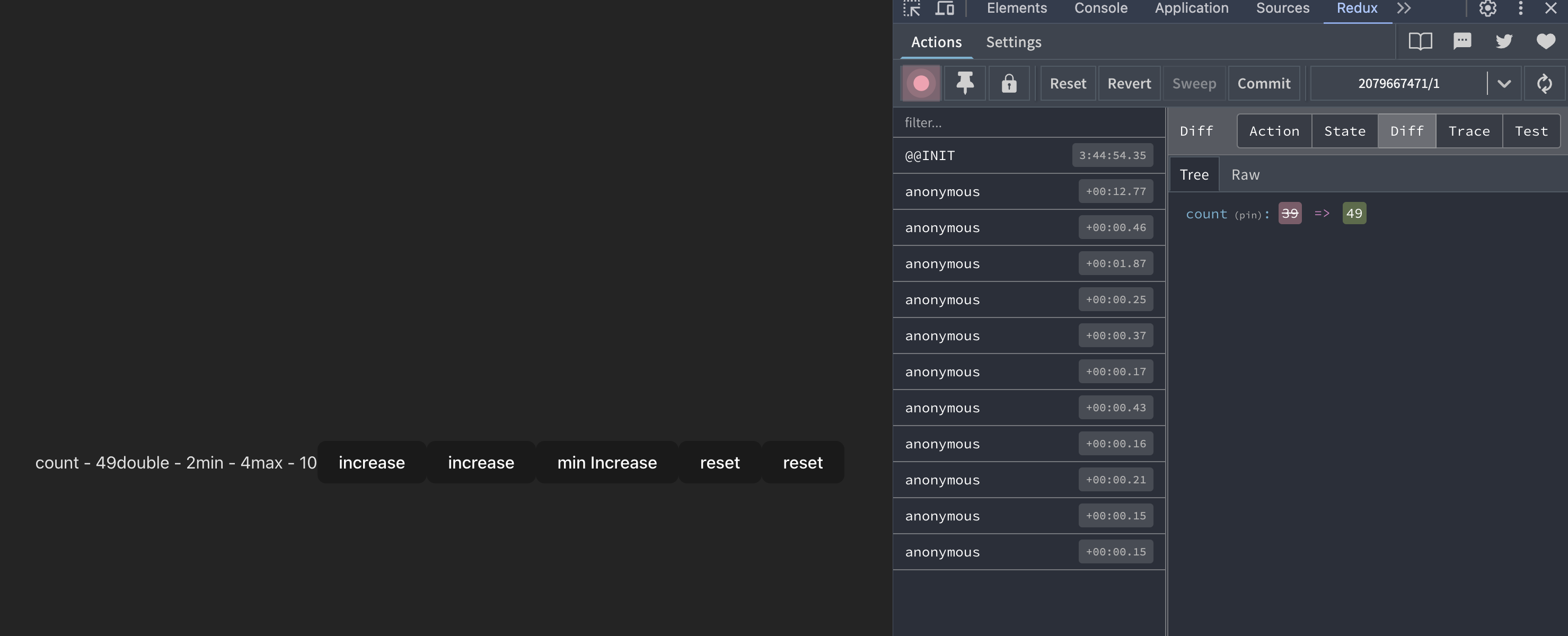
개발자 도구 ( Devtools )
Redux DevTools 와 같이 Zustand 의 상태를 모니터링할 수 있는 개발자 도구를 사용할 수 있습니다.
Zusthand 에서 middleware 로 제공하는 devtools 함수를 이용하시면, 개발자 도구가 활성화 됩니다.
import { create } from 'zustand'
import { combine, devtools } from 'zustand/middleware';
const initialState = {
count: 1,
double: 2,
min: 0,
max: 10
}
export const useCountStore = create(
devtools(combine(
initialState,
set => ({
actions: {
increase: (value = 1) => set(state => ({count: state.count + value})),
decrease: () => set(state => ({count: state.count - 1})),
minIncrease: () => set(state => ({min: state.min + 1})),
resetState: (keys?: Array<keyof typeof initialState>) => {
if (!keys) {
set(initialState)
return
}
keys.forEach(key => {
set(({[key] : initialState[key]}))
})
}
}
})
))
)
'라이브러리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lombok (1) | 2025.02.04 |
|---|---|
| Tanstack Query (4) | 2024.10.02 |
| axios Interceptors (4) | 2024.09.01 |
| Jotai (1) | 2024.08.24 |
| React Intersection Observer (0) | 2024.08.20 |